Joint pain or arthralgia occurs in a number of diseases and its mechanism is not yet fully understood. Joint elements (ligaments, cartilage, capsule, bones) have pain receptors and react to inflammatory processes and mechanical irritation. When moving, the joint receptors are stimulated, signals from them reach the brain and the person feels pain. When there is inflammation, the receptors react more sensitively to irritation because cells of the immune system release pain-conducting substances.
Typically, joint pain is not accompanied by swelling of the surrounding soft tissue, contour deformation, or redness. When the joints are palpated, the pain is moderate. In some cases, there are no obvious signs of inflammation on the x-ray. There are also no complaints about a pronounced restriction in the mobility of large joints.
Arthralgia is often associated with rheumatic diseases. In this case, the joints ache and hurt during changes in the weather. Severe problems in the knee and hip joints occur more often. In the morning, the patient is unable to get up immediately and walk briskly due to stiffness and pain in the joints.
If the pain in the joints is paroxysmal, occurs unexpectedly, increases within a day, lasts for several days and only one joint hurts, we can assume arthritis due to gout. Uric acid crystals accumulate in joint tissue and irritate the tissue, causing pain.
If arthralgia occurs in large joints (knees, hips), grows slowly, becomes stronger during physical work and is accompanied by morning stiffness, then degenerative-dystrophic changes can be diagnosed - arthrosis.
causes
Joint pain has various causes. One of the most common causes of arthralgia is acute infection. Aching pain in the joints can occur before the first signs of the disease or in its early stages. Joint fractures throughout the body often occur during an infectious process. At the same time, the amplitude of movements in them does not change.
Post-infectious severe arthralgia occurs in genitourinary and intestinal infections.
Joints suffer from secondary syphilis, endocarditis and tuberculosis. If there are chronic sources of infection in the body, for example in the kidneys, bile ducts, pelvic organs, parasitic diseases, then the joints also hurt.
Common causes of joint pain include:
- Thyroid diseases.
- Poisoning with heavy metal salts.
- Physical injuries.
- Long-term use of certain medications.
I am worried about joint pain due to various diseases. They are divided into 2 large groups:
- Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints caused by infections, autoimmune processes, dysfunction of the endocrine glands and metabolism.
- Osteoarthritis is a disease that involves the destruction of the articular cartilage and the underlying articular surfaces of the bones. Over time, the cartilage becomes rough, loses elasticity and tears.
The classification of joint diseases into arthritis and arthrosis is conditional. Without treatment, arthritis eventually turns into osteoarthritis because inflammatory processes disrupt the metabolism in the cartilage. They do not receive adequate nutrition, become thinner quickly and gradually collapse.
In the case of osteoarthritis, which is initially accompanied by physical overload of the joint, inflammation develops over time. It arises from the accumulation of cartilage and bone tissue fragments in the joint cavity and the triggering of inflammatory reactions.
The risk group for the development of this pathology includes:
- Women in menopause.
- Older people with pronounced age-related changes in the body.
- Obese patients.
- Patients with a history of joint trauma.
- Athlete.
- People with certain professions. For example, the knee joint often suffers from people who spend long hours on their feet (teachers, surgeons, hairdressers, etc. ). Wrist pain is a common symptom among musicians, cashiers, and loaders who make monotonous movements with their hands.
species
There are different classifications of joint pain. Depending on the localization of arthralgia, the following are distinguished:
- Mono-arthralgia (1 joint hurts).
- Oligo-arthralgia (affects 2-5 joints).
- Polyarthralgia (pain in more than 5 joints).
Depending on the location of the joints, arthralgia is divided into general and localized.
The nature of arthralgia is:
- Spicy and boring.
- Temporary and permanent.
- Weak, moderate and intense.
Characteristics and conditions for the occurrence of arthralgia depend on the diagnosis. The most common signs of joint pain are:
- Starting.Arthralgia initially occurs when walking and then disappears when moving. It is associated with the friction of the articular surfaces of the bones, which are covered with destroyed cartilage tissue. After a few steps, this mass accumulates in the inversions of the joint capsule and the arthralgia disappears.
- pain.They appear after physical work of the joints and disappear when at rest.
- Night.They indicate severe joint damage and are caused by blood congestion pressing on the bone tissue beneath the cartilage. After a night's sleep, there is a feeling of stiffness in the joints and the symptoms disappear with movement.
- Permanently.Occurs when there is inflammation of the joint capsule.
- Suddenly (joint blockage). Caused by a piece of bone or cartilage becoming stuck between two joint surfaces.
- migration.First one joint hurts, then the pain shifts to the other.
- Reflects.They are not felt in the affected joint, but in a neighboring one. For example, if you suffer from hip joint disease, your knee will hurt.
diagnosis

If you suffer from arthralgia, you should not self-medicate. If you have joint pain, be sure to consult your doctor to make the diagnosis. After the main examination, he will refer you to an orthopedist-traumatologist or rheumatologist for a consultation. If a previously injured joint becomes diseased, consultation with a surgeon is indicated.
When visiting a doctor, it is important to talk about the following points:
- When pain occurs.
- From here the pain decreases and subsides.
- How often do painful attacks occur?
- Arthralgia occurred for the first time or had already existed.
- Is there hyperemia, swelling or deformation of the joint?
- Have you had stress, acute respiratory illnesses or heavy physical activity in the last few days?
This information helps the specialist draw conclusions about the condition of the patient's joints and make a diagnosis.
After the doctor has determined the nature of the joint pain, he will order an examination and issue a referral for:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Blood chemistry.
- Immunodiagnostics.
- X-ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound of the joints.
- If necessary, biopsy of the damaged tissue.
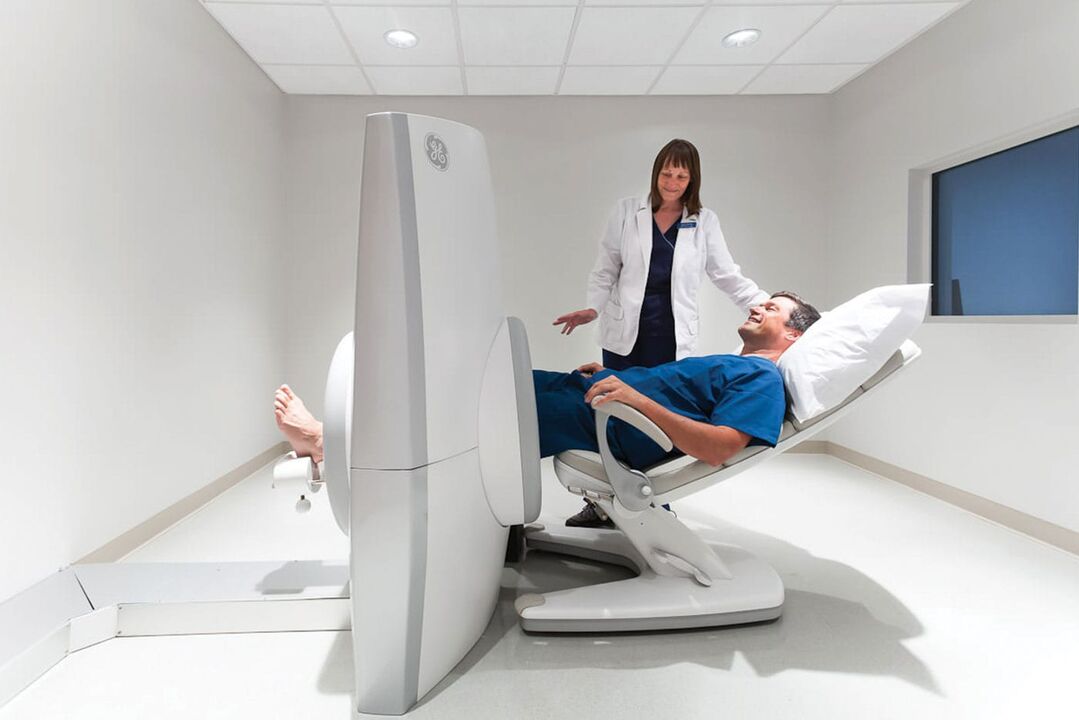
X-ray of the joints. This method allows you to examine the joint in two projections and perform radiopaque arthrography.
Using MRI and CT, you can assess in detail the condition of osteochondral structures and soft tissues.
Ultrasound of joints. Helps in detecting effusions in the joint cavity, erosions of the articular surfaces of bones, changes in the synovial membrane and assessing the width of the joint spaces.
Invasive examination methods. If necessary, a joint puncture and synovial biopsy are performed. In difficult cases, arthroscopy (examination of the joint cavity from the inside) is carried out.
Laboratory tests help detect signs of inflammation and rheumatic pathology. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the content of C-reactive protein, uric acid, antinuclear antibodies, rheumatoid factor and ACCP are determined in the peripheral blood. The synovial fluid is subjected to microbiological and cytological analysis.
Treatment
For joint pain, treatment should be comprehensive. Tactics include reducing mechanical stress on the joint, eliminating inflammation, and preventing progression of the underlying disease. This is the only way to slow down cartilage degradation, maintain joint mobility and improve the quality of life of a patient with arthralgia.
To relieve joint pain, the following is prescribed:
- Painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Physiotherapy (shock wave therapy, ozone therapy, myostimulation, phonophoresis).
- Therapeutic exercise.
- Massage.
- Acupuncture.
- Orthopedic or surgical correction.
Conservative therapy uses non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; they relieve pain and have an anti-inflammatory effect. Chondroprotectors slow down the development of osteoarthritis. These medications reduce inflammation and prevent further degeneration of the cartilage in the joints. These include cartilage components – chondroitin, glucosamine. Chondroprotectors promote restoration processes in cartilage tissue.
To eliminate spasms of skeletal muscles, muscle relaxants are prescribed.

When arthritis is associated with infection, antibiotics are indicated.
For good joint function and recovery processes, complexes of vitamins and minerals are also prescribed. Vitamins A, C, E, group B as well as the minerals calcium and selenium are particularly important.
In case of severe inflammation and lack of treatment effect, glucocorticosteroids are prescribed according to the scheme.
The drug treatment is supplemented with warming, pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory ointments.
If the arthralgia is very severe, a block of the nerve endings is performed. To do this, they use effective medications that make joint pain forgotten for a long time.
To reduce arthralgia, the joints are protected from overload. Prolonged standing, lifting and carrying heavy objects puts strain on the joints that far exceeds the permissible load and leads to cartilage damage.
To prevent arthralgia, follow these rules:
- Normalize your body weight.
- Wear comfortable low-heeled shoes; if you have flat feet, use orthopedic insoles.
- Avoid psycho-emotional and physical overload.
- Change your posture more often while working, take five minutes to move and relieve muscle tension.
- To maintain physical activity, choose moderate exercise. Alternating mobility with rest periods.
- Do regular exercises that relieve pressure on your joints. For example, you can bend and straighten your legs while sitting or lying down for 20-30 minutes and do the "bicycle" exercise. After that, rest for 7-10 minutes to improve blood circulation. These exercises help strengthen the cartilage in your bodythe leg joints.
In severe cases, surgical treatment is necessary. The doctor removes necrotic tissue from the joint cavity through small incisions. If fluid has accumulated in the joint, a puncture is performed.
To reduce the load and increase mobility of the diseased joint, a periarticular osteotomy is performed. The bones forming the joint are sawn off so that they then grow together with a certain inclination.
In severe cases, a joint replacement is performed.
prevention

Follow these recommendations to prevent joint diseases:
- If you are obese, normalize your body weight.
- Drink at least 1. 5-1. 7 liters of water per day.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Lead an active lifestyle.
- Avoid excessive alcohol and tobacco consumption.
- Night sleep should last at least 8 hours.
- Walk outdoors as often as possible.
- Try to change your posture more often.
Summary
According to statistics, arthralgia of the upper and lower extremities occurs in half of people over 40 years old. In patients over 70 years old, joint diseases are observed in 90% of cases. If a joint suddenly hurts, consult a doctor immediately to find out the causes and prescribe treatment. Take care of your joints and load them with useful activity. Only physical exercise can keep your joints flexible, even if the cartilage is damaged and the movement causes discomfort.


















